2 September, 2025

The production technique of the artificial marble is one of the most curious inventions of present-day building materials. Knowledge of the processes involved in the manufacturing of the artificial marble is of importance as one gets to appreciate why this engineered stone has gained popularity as a countertop, flooring, and even architectural material in markets all over. Artificial marble manufacturing, especially when used for applications like artificial marble countertop and artificial marble for kitchen, reveals the material's adaptability and value. While there are canned explanations of artificial marble manufacturing, this detailed piece takes you through the intricate process that involves the making of artificial marble in terms from the selection of raw materials to the finishing of the product.
What Is Artificial Marble?
Artificial marble, often called engineered marble, cultured marble, or synthetic marble, is an engineered material, identified as a composite material, created to imitate the look and characteristics of natural marble stone. Artificial marble slabs offer a consistent look and customizable strength, making them perfect for both commercial and residential projects. Artificial marble production differs from the production of natural marble quarried and, to an extent, from the processing of natural marble, where, by a combination of materials such as natural marble chips, resins, pigments, and additives, a homogeneous, durable surface material is created.
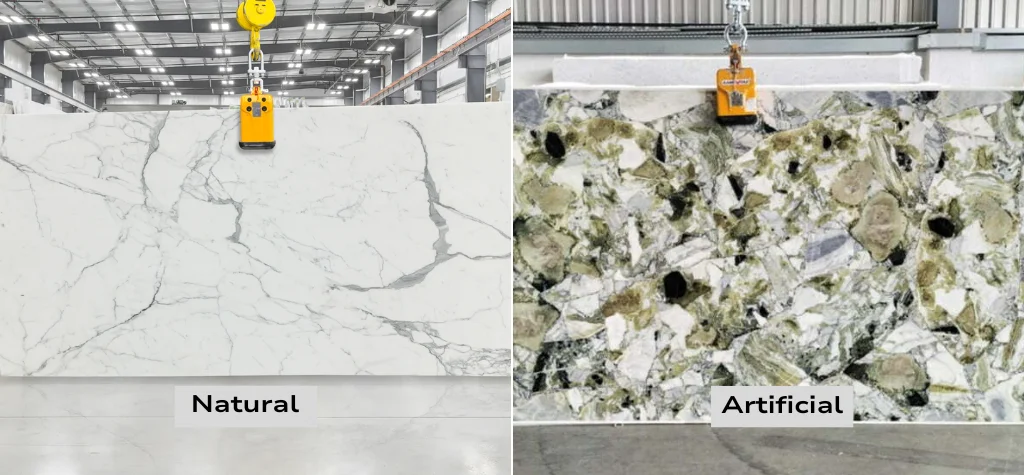

Related to this is the fact that the artificial marble technology was developed due to the shortcomings of natural marble in terms of being porous, having irregular patterns, and structural inadequacies. The current modern manufacturing of artificial marble offers better consistency, durability, and flexibility to customize when compared to conventional natural stone varieties, including sought-after styles like artificial white marble or artificial onyx marble.
Raw Materials Used in Artificial Marble Production
The artificial marble manufacturing process begins with careful selection of high-quality raw materials, each contributing specific properties to the final product.
-
Natural Marble Chips and Powder: The base material of artificial marble is heavily crushed natural marble that can be in any size, but is mostly fine powder to chip size, which is hitting several millimeters. These pieces of marble are obtained using quarries all over the world, which give such types of marble their natural look and features that otherwise would make artificial marble look beautiful, especially in premium variants like white artificial marble or artificial marble white options.
-
Polymer Resins: Artificial marble is composed mainly of unsaturated polyester or acrylic-based resins as the binder, called high-performance polymer resins. These resins form the structural integrity that is required to make it durable and can be shaped and molded to any thickness and overall shape.
-
Pigments and Colorants: Advanced pigments and colorants allow manufacturers to create almost any combination of color schemes or patterns. Mixing of these additives is done in a measured proportion so as to ensure a coherent color appearance throughout the artificial marble slab.
-
Catalysts and Hardeners: The curing process is regulated by chemical catalysts and hardening agents so that the right chemical reactions happen during the manufacturing process. The components specify the time of setting and the final hardness properties of the artificial marble.
-
Additives and Fillers: Depending on the required properties, numerous additives are used, such as flame retardants, UV stabilizers, performance enhancers and so on, to provide the required properties. To change density and thermal properties, mineral fillers can also be added.
The Artificial Marble Manufacturing Process
Step 1: Material Preparation and Mixing
The mass production process of man-made marbles starts with careful measuring and preparation of all materials. High-level computerized systems make the proportions of batches similar and maintain the quality standards of the production.
The cleaning and size-sorted natural marble chips are used to eliminate impurities and obtain uniformity of distribution. The polymer resins would be mixed to a definite viscosity, and the pigments also would be pre-mixed to get a definite color maintenance.
Step 2: Blending and Homogenization
Machinery used to mix industry incorporates the materials previously prepared in a measured percentage. This is a tense moment which may not be timed well and there has to be perfect control of temperature to timely cure and at the same time achieve perfect homogenizing of each element.
The mixing is normally done in big industrial mixers, making it able to deal with large volumes, but still such that there is a constant distribution of the materials being mixed. The mixing blades are specialized to mix marble chips, resins and additives significantly well, but they cannot destroy the natural stone pieces.
Step 3: Molding and Forming
After a good mix has been achieved, artificial marble goes into the mold-making process, where it acquires its final form. The way in which an artificial marble slab is made depends on the nature of the intended use and the desired thickness.
-
Compression Molding: In the case of standard slabs, so much of the material is poured into big molds and compressed under hydraulic forces. This compression process helps in the elimination of air bubbles and therefore makes the slab have an even density.
-
Vibration Compaction: Molding with purposeful vibration allows the material to smooth and removes air from the air that causes a denser product to be formed and ensures strong final products. The frequency and period of vibration are also controlled accurately in order to have the best properties of the material.
Step 4: Curing and Hardening
The process of curing is one of the most important stages in artificial marble production. The right chemical reaction between resins and hardening agents is made possible by controlled temperature and humidity conditions.
-
Initial Curing: The molded artificial marble is cured at a high temperature of about 60-80°C, and this process also takes a number of hours. The process begins at this stage, where the polymerization process leads to the formation of the polymer structure that lends strength to manmade marble.
-
Complete Curing: Prolonged curing times, such as 24-48 hours, are useful to get a full curing reaction and good properties of the material. They can use temperature cycles, which improve the curing process and do away with internal stresses.
Step 5: Demolding and Initial Processing
Artificial marble slabs after full curing are washed out well out of the molds and a basic quality check is carried out. At this point, any surface blemishes or abnormalities are determined and resolved.
-
Surface Preparation: The first step of the surface preparation consists in addition to the removal of any mold release agents in preparing the surface for further processing procedures. This process guarantees the best grip in any form of surface treatment or coating.
Step 6: Cutting and Shaping
The artificial marble is cut with the help of precision cutting machines such as diamond-blade saws and water-jet cutters, to the required sizes. The used CNC machines help to create difficult shapes and individual designs to serve a certain project.
-
Edge Processing: Special machines make edges in a diversity of ways, including straight and simple to decorative and detailed. The cutting process requires very precise control of feed rates and cooling so as to avoid thermal damage to the material.
Step 7: Surface Finishing
Artificial marble has an ultimate look and feel formulated by the surface finishing phase. There are various finishes that will be available based on the planned application and desired aesthetic.
-
Polishing: Progressive polishing steps utilizing finer and finer abrasives provide the typical glossy finish that is believed to be of quality artificial marble. Polishing machines are controlled by a computer that provides uniformity of the surface on the entire slab.
-
Texturing: Textured finishes, such as matte or brushed, textured finish can be made by special processing procedures. Such finishes provide variable aesthetic choices with the possibility of better slip resistance in flooring use.
Step 8: Quality Control and Testing
A thorough quality standard procedure is carried out to ensure that each of the artificial marble slabs conforms to the standard given performance levels. Some of the properties evaluated in the testing protocols include:
-
Physical Properties: Density, porosity, and dimensional stability testing verify structural integrity and consistency.
-
Mechanical Properties: Flexural strength, impact resistance, and abrasion resistance testing ensure durability under intended use conditions.
-
Chemical Resistance: Exposure testing to various chemicals and staining agents confirms suitability for specific applications.
-
Visual Quality: Color consistency, pattern uniformity, and surface finish quality are evaluated against established standards.
Quality Assurance in Artificial Marble Manufacturing
Strict quality control standards are implemented at all points throughout the production of artificial marble. Statistical process control tools check essential parameters during the production process so that the quality and performance attributes will always remain stable.
-
Incoming Material Inspection: Raw consumption material testing involves testing all the material to be employed during production and testing involves classroom testing, testing chemical composition, particle size distribution, and purity level testing.
-
In-Process Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of mixing ratios, curing temperatures, and processing parameters ensures adherence to established specifications.
-
Final Product Testing: The finished slabs of artificial marble are thoroughly tested by industry practice and customer demands.
Why Artificial Marble Is a Popular Choice for Modern Interiors
The ways of artificial marble have taken strides compared to its customary days. Its versatility, in terms of affordability, durability, and elegance, has made it a leading candidate against several other applications to include:
-
Kitchen Countertops: Thanks to its heat and stain resistance, especially in designs made from artificial marble white and artificial marble for kitchen collections.
-
Bathroom Vanities: Non-porous and easy to clean.
-
Flooring and Wall Cladding: Seamless, luxurious designs for entire spaces.
-
Commercial Settings: Durable enough for high-traffic areas yet aesthetically pleasing.
Additionally, artificial marble price points make it a practical alternative to natural stone, especially in cost-sensitive markets. For those seeking refined elegance in surface finishes, Alaska Surfaces, a leading tile manufacturer and supplier, offers a wide range of tiles finishes such as glossy, matte, textured, and high-gloss marble-look tile. Their versatile collection beautifully mimics the aesthetic of natural marble while offering enhanced performance and durability for both residential and commercial interiors.
Conclusion
Learn to make artificial marble to know the high level of engineering and the accuracy in production of the material that is versatile in nature. Raw material selection, production, finishing and all other stages of artificial marble manufacturing help in developing high performance surface material that mixes both the beauty of natural marble with increased durability and consistency.
The future of the techniques of producing artificial marble holds even higher expectations of quality, sustainability, and imagination in design. With the evolution of manufacturing processes, artificial marble will go on to produce high-quality products that are thus able to offer alternatives to natural stone to architects, designers, and homeowners.
This insider account of the industrial process related to artificial marble production explains why this artificial hard facing has gained popularity not only in residential but also in commercial use spectrums. The material science, accuracy, manufacturing and quality control are balanced very carefully, which leaves the final product to satisfy the expectations of the challenging modern construction and design jobs.